The Fine Line of Fencing: What You Need to Know About Property Boundaries and the Law
Here's an overview:
- Introduction to Fencing Laws: Importance and General Considerations
- Know Your Boundaries: Defining Property Lines
- Understanding Height Restrictions for Fences
- Navigating the Permit Process: Do You Need One for Fencing?
- Addressing the 'Good Neighbor' Fence Embrace and Shared Boundaries
- Fencing and Public Right-of-Way: What You Need to Know
- Resolving Disputes: How to Handle Fencing Rows with Neighbors
- Privacy vs. View: Balancing Rights and Considerations
- The Role of Homeowners’ Associations in Fencing Regulations
- Safety Provisions: Pool Fencing and the Law
- Concluding Thoughts: Best Practices for Responsible Fencing
Introduction to Fencing Laws: Importance and General Considerations

- Local Zoning Regulations: Understand local ordinances that dictate fence height, materials, and aesthetics.
- Boundary Surveys: A professional survey can clarify property edges before fence erection.
- Shared Fences: Collaborate with neighbors when a fence sits on a property line.
- Permits: Obtain necessary permits to comply with local building codes.
- Visibility and Safety: Ensure fences do not obstruct sightlines for drivers or pedestrians.
Know Your Boundaries: Defining Property Lines

- Refer to their property deed, which includes a detailed description of property boundaries.
- Obtain a plat, a map drawn to scale of their land, from the county recorder's office.
- Consider hiring a professional land surveyor for an accurate assessment.
- Consult with local zoning laws to ensure compliance with setback regulations.
- Discuss plans with neighbors to avoid disputes and maintain good relations.
Understanding Height Restrictions for Fences
 When erecting a fence, homeowners must be aware of local zoning laws dictating height limits. Municipalities often have specific ordinances to maintain community aesthetics and sightlines. Typically, front yard fences are limited to a lower height than those in backyards to preserve the open feel of a neighborhood. For instance, front yard fences may be restricted to 3 or 4 feet, while backyard fences could be 6 feet or higher. It is important to obtain the necessary permits and adhere to these regulations to avoid legal disputes or the need to modify or remove an improperly built fence. Furthermore, corner lots often have more stringent rules due to visibility concerns for traffic safety. Checking with local zoning boards or planning departments is essential before construction to ensure compliance with all height restrictions.
When erecting a fence, homeowners must be aware of local zoning laws dictating height limits. Municipalities often have specific ordinances to maintain community aesthetics and sightlines. Typically, front yard fences are limited to a lower height than those in backyards to preserve the open feel of a neighborhood. For instance, front yard fences may be restricted to 3 or 4 feet, while backyard fences could be 6 feet or higher. It is important to obtain the necessary permits and adhere to these regulations to avoid legal disputes or the need to modify or remove an improperly built fence. Furthermore, corner lots often have more stringent rules due to visibility concerns for traffic safety. Checking with local zoning boards or planning departments is essential before construction to ensure compliance with all height restrictions.
Navigating the Permit Process: Do You Need One for Fencing?

- Height and length of the fence
- Materials used
- Proximity to public property
- Historical district restrictions
- Consult with their local building authority or zoning office for specific regulations.
- Review their property's deed for any easements or restrictions.
- Check with their homeowners' association, if applicable, for additional guidelines.
- Ensure that the planned fence will not encroach upon neighbor's property.
Addressing the 'Good Neighbor' Fence Embrace and Shared Boundaries
 When neighbors share a boundary, clear communication and mutual agreements become essential. The 'Good Neighbor' Fence Act often governs fence construction and maintenance, requiring neighbors to:
When neighbors share a boundary, clear communication and mutual agreements become essential. The 'Good Neighbor' Fence Act often governs fence construction and maintenance, requiring neighbors to:
- Share equally in costs and maintenance responsibilities
- Notify each other of any intended boundary changes or fence repairs
- Resolve disputes through negotiation or mediation to avoid litigation
Fencing and Public Right-of-Way: What You Need to Know
 When installing a fence, understanding the public right-of-way (ROW) is crucial. ROW is typically land reserved for streets, alleys, and sidewalks, and its primary use is for public passage. Here are key aspects to consider:
When installing a fence, understanding the public right-of-way (ROW) is crucial. ROW is typically land reserved for streets, alleys, and sidewalks, and its primary use is for public passage. Here are key aspects to consider:
- Local Regulations: Verify with local authorities to understand the specific ROW regulations and required setbacks before erecting your fence.
- Permits: Acquiring a fencing permit may be necessary. Failure to do so can lead to fines or removal orders.
- Encroachment: Placing a fence within the ROW without permission is considered encroachment, potentially leading to legal disputes.
- Survey: Conduct a professional survey to determine property lines accurately, ensuring your fence does not intrude on the ROW.
- Visibility: Ensure that the fence does not obstruct driver visibility at crossroads or driveways.
Resolving Disputes: How to Handle Fencing Rows with Neighbors
 In tackling fencing disputes, a composed approach is key. Initially, review property deeds and local regulations to affirm boundary lines. If ambiguity persists, consider a professional land survey. Neighborly dialogue, grounded in mutual respect, often resolves issues. When direct discussions falter, mediation through a third party is a productive avenue. As a last resort, legal counsel can guide you through potentially necessary litigation. Throughout the process, documenting all communications and agreements is essential for safeguarding your interests.
In tackling fencing disputes, a composed approach is key. Initially, review property deeds and local regulations to affirm boundary lines. If ambiguity persists, consider a professional land survey. Neighborly dialogue, grounded in mutual respect, often resolves issues. When direct discussions falter, mediation through a third party is a productive avenue. As a last resort, legal counsel can guide you through potentially necessary litigation. Throughout the process, documenting all communications and agreements is essential for safeguarding your interests.
Privacy vs. View: Balancing Rights and Considerations
 When erecting a fence, homeowners often grapple with the dual desires for privacy and preserving views. On one hand, a fence can offer a sense of seclusion, shielding residents from the eyes of neighbors and passersby. However, this privacy can come at the cost of obstructing scenic vistas, both for the homeowner and their neighbors. Property laws generally promote mutual respect among neighbors, advocating for a balance between privacy and preserving views. Homeowners are encouraged to communicate with adjacent property owners when planning a fence that may affect shared sightlines. This collaboration can lead to creative solutions that maintain privacy without completely sacrificing views, such as lattice designs that provide a screen without a solid barrier, or varied fence heights that block sightlines selectively. Additionally, local ordinances often address the height and type of fences allowed and may include specific provisions about maintaining views, particularly in picturesque or historic areas. Thus, understanding and navigating these regulations is essential when designing a fence that is both legally compliant and considerate of the rights and preferences of neighbors. In the end, finding a compromise that respects the privacy and views of all involved parties is not only neighborly but legally prudent. By taking a collaborative approach and remaining informed about local laws, homeowners can erect fences that reflect a judicious balance between personal seclusion and communal harmony.
When erecting a fence, homeowners often grapple with the dual desires for privacy and preserving views. On one hand, a fence can offer a sense of seclusion, shielding residents from the eyes of neighbors and passersby. However, this privacy can come at the cost of obstructing scenic vistas, both for the homeowner and their neighbors. Property laws generally promote mutual respect among neighbors, advocating for a balance between privacy and preserving views. Homeowners are encouraged to communicate with adjacent property owners when planning a fence that may affect shared sightlines. This collaboration can lead to creative solutions that maintain privacy without completely sacrificing views, such as lattice designs that provide a screen without a solid barrier, or varied fence heights that block sightlines selectively. Additionally, local ordinances often address the height and type of fences allowed and may include specific provisions about maintaining views, particularly in picturesque or historic areas. Thus, understanding and navigating these regulations is essential when designing a fence that is both legally compliant and considerate of the rights and preferences of neighbors. In the end, finding a compromise that respects the privacy and views of all involved parties is not only neighborly but legally prudent. By taking a collaborative approach and remaining informed about local laws, homeowners can erect fences that reflect a judicious balance between personal seclusion and communal harmony.
The Role of Homeowners’ Associations in Fencing Regulations

Homeowners’ Associations (HOAs) often exert significant influence over fencing regulations within their governed communities. When installing fences, homeowners must comply with:
- HOA covenants, conditions, and restrictions (CC&Rs): which may dictate fence height, style, color, and materials to ensure aesthetic uniformity.
- Approval processes: Many HOAs require residents to submit fence plans for approval before installation to conform to community standards.
- Maintenance Guidelines: HOAs may enforce maintenance rules to preserve property values and community appearance.
Safety Provisions: Pool Fencing and the Law
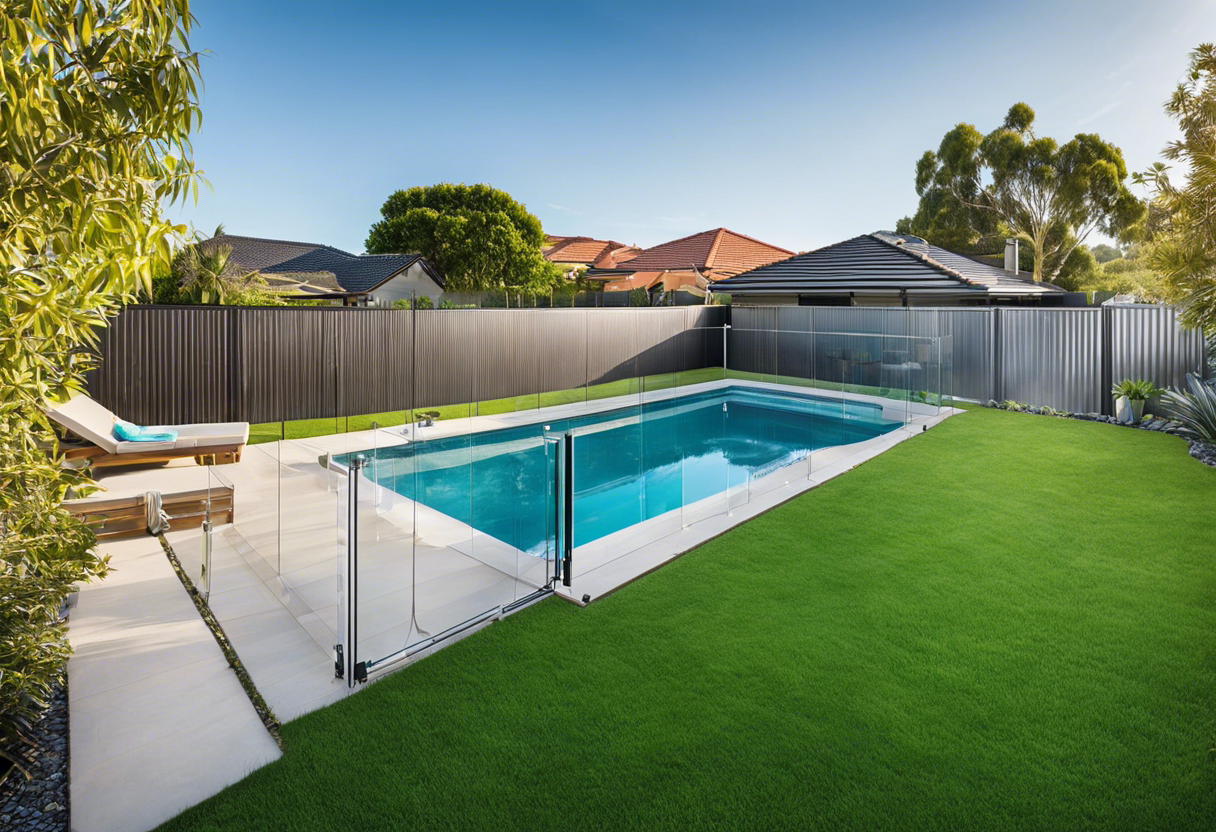

When installing a pool, homeowners must understand that pool fencing isn't merely a safety feature; it's often mandated by law. Regulations vary by location but generally require:
- A fence of a certain height, typically 4 feet or higher
- Self-closing and self-latching gates
- Latches placed high enough to be out of children's reach
Concluding Thoughts: Best Practices for Responsible Fencing

When it comes to fencing and property boundaries, responsible practices are paramount. Individuals should:
- Engage in clear dialogue with neighbors to maintain harmonious relationships.
- Research and comply with local zoning regulations to ensure legal conformity.
- Obtain proper surveys to accurately determine property lines, avoiding disputes.
- Respect environmental considerations by selecting sustainable materials and preserving local wildlife habitats.
- Opt for professional installation to guarantee structural integrity and compliance with standards.
- Remain vigilant about maintenance, which promotes safety and extends the life of the fence.
- Consider the aesthetics of the neighborhood to support community values and property values.
















